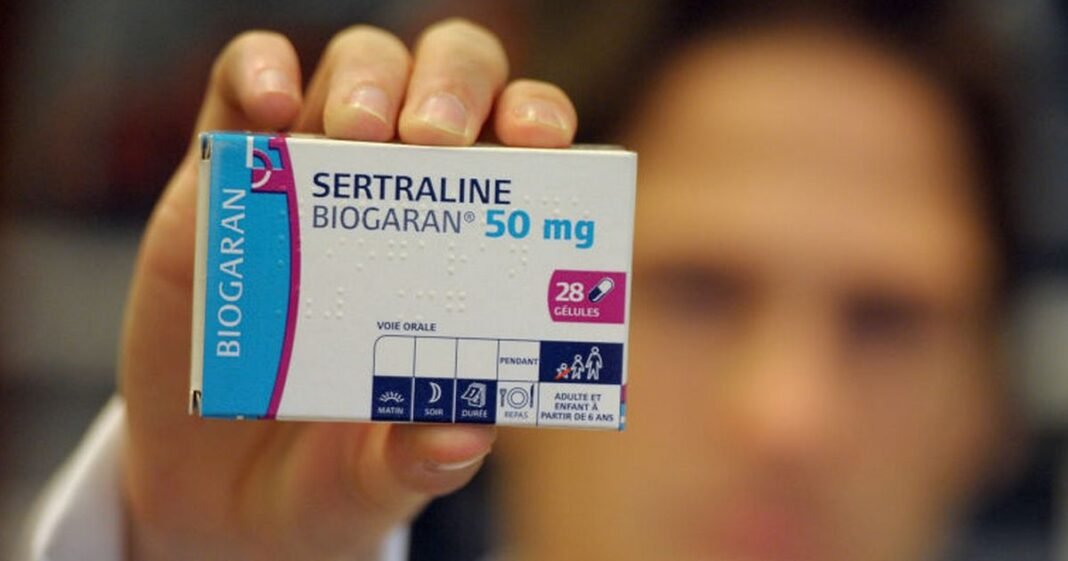
Millions of individuals taking a common prescription medication have received a crucial warning about avoiding a particular fruit. Recent statistics indicate that over 24 million sertraline prescriptions were dispensed in England in 2024, making it the most prescribed antidepressant in the country.
Although sertraline is widely used for various mental health conditions in the UK, the total number of prescriptions does not directly equate to the number of individuals using the drug. Sertraline, classified as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), is prescribed to treat conditions such as depression, OCD, panic disorder, PMDD, PTSD, and SAD.
According to the NHS, sertraline functions by boosting serotonin levels in the brain, aiding in the management of depression with fewer adverse effects compared to older antidepressants. Antidepressants address mental health symptoms but are usually combined with therapy for more severe cases to address underlying issues.
Consuming grapefruit or its juice while on antidepressants, including sertraline, can heighten drug levels in the body, possibly resulting in intensified side effects. Grapefruit inhibits an enzyme that helps metabolize medications, leading to elevated drug concentrations and increased risks of adverse effects and toxicity.
Higher doses of sertraline may lead to dangerous changes in heart rhythm and potential complications like kidney damage, muscle issues, and respiratory problems. Avoiding grapefruit, Seville oranges, pomelos, and limes is crucial when taking antidepressants, as these fruits can interact similarly to grapefruit.
Apart from sertraline, other antidepressants like fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, amitriptyline, and trazodone can also be affected by grapefruit consumption. It is advisable to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider before initiating new medications to ensure optimal safety and efficacy.
Understanding potential food and drug interactions is essential to safeguard one’s health while undergoing treatment. Seeking guidance on dietary adjustments or medication administration can help mitigate risks associated with drug interactions.